Outline of the Article
Introduction
Understanding the Basics
Types of Cabinet Air Conditioners
Key Features of Cabinet Air Conditioners
Applications of Cabinet Air Conditioners
Advantages of Using Cabinet Air Conditioners
Challenges and Considerations
Choosing the Right Cabinet Air Conditioner
Installation Process
Maintenance and Care
Innovations in Cabinet Air Conditioning
Comparing Cabinet Air Conditioners to Other Cooling Systems
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Future Trends in Cabinet Air Conditioning
Conclusion
FAQs
Introduction
In the realm of modern technology, cabinet air conditioners play an essential role in maintaining optimal operating conditions for various electronic and industrial equipment. But what exactly are these devices, and why are they so crucial? Let's dive into the world of cabinet air conditioners to understand their significance, functionality, and applications.
Understanding the Basics
Definition of Cabinet Air Conditioners
Cabinet air conditioners (cabinet ac units) are specialized cooling systems designed to control the temperature within enclosed spaces, such as electrical cabinets, server racks, and other equipment housings. Unlike traditional air conditioners, which cool entire rooms or buildings, cabinet air conditioners focus on specific areas that require precise temperature regulation.
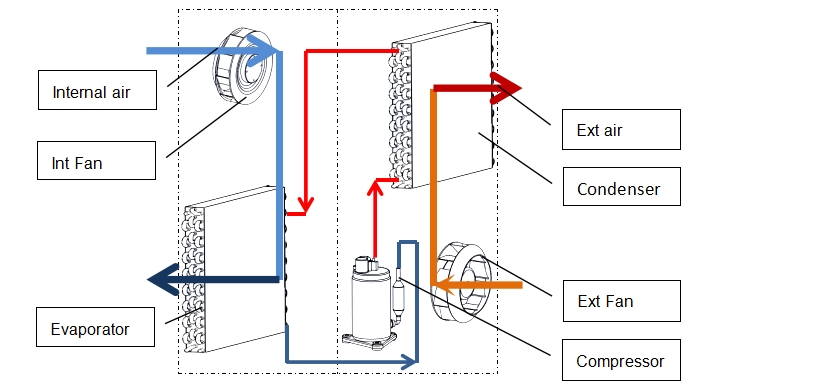
How Cabinet Air Conditioners Work
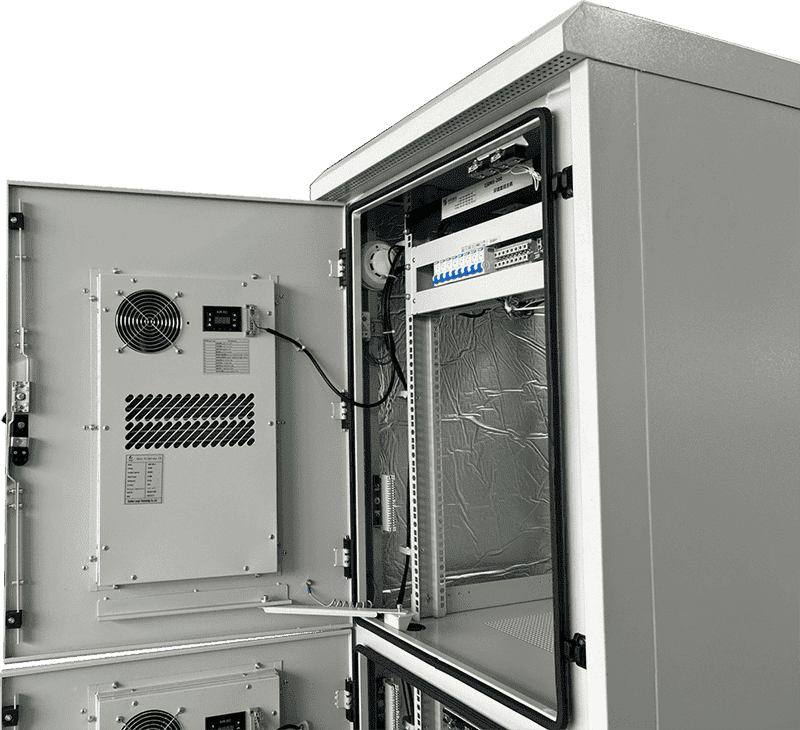
The cabinet air conditioner (cabinet cooling unit) or enclosure air conditioner features a downward air outlet and an upward air return system, utilizing a backward inclined centrifugal turbine fan. During operation, the centrifugal fan draws air pressure from the upper part of the cabinet downward, creating higher air pressure in the lower part and facilitating rapid air circulation. This strong convection mode can naturally cool the cabinet and reduce hot spots, even when the compressor is not active. Additionally, the fan air volume of the cabinet air conditioner is generally more than three times that of a household air conditioner, resulting in significantly better heat dissipation.
Types of Cabinet Air Conditioners
Self-Contained Cabinet Air Conditioners
Self-contained cabinet ac units (enclosure cooling systems) are compact and integrate all necessary components, such as the compressor, evaporator, and condenser, within a single enclosure. They are easy to install and ideal for smaller spaces or individual cabinets.
Split System Cabinet Air Conditioners
Split systems separate the components into two units: the evaporator inside the cabinet and the condenser outside. This configuration is suitable for larger installations where space within the cabinet is limited.
Thermoelectric Cabinet Air Conditioners
Thermoelectric ac units use the Peltier effect to create a temperature differential, making them ideal for applications requiring precise temperature control without moving parts or refrigerants.

Key Features of Cabinet Air Conditioners (Enclosure AC Units)
Cooling Capacity
The cooling capacity of a cabinet air conditioner (cabinet ac) is measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs) or kilowatts (kW), indicating how much heat it can remove per hour. Selecting the right capacity is crucial for efficient cooling.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a key consideration, with modern units designed to consume less power while delivering optimal performance. Look for units with high Energy Efficiency Ratios (EER) or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratios (SEER).
Noise Levels
Noise levels are important, especially in environments where quiet operation is essential. Many cabinet air conditioners are designed to operate silently to minimize disruption.
Cytech's Cabinet Air Conditioner (Enclosure AC) Datasheet
DC cabinet air conditioner (DC enclosure ac unit)
Model | Voltage | Nominal cooling capacity(W) (L35/L35) | Nominal cooling capacity(Btu/hr) (L35/L35) | Power consumption(W)(L35/L35) | IP Grade | Heater (W)(option) | Internal air flow (m3/h) | Refrigerant | Noise (dbA) |
CYDC105-1 | -48VDC(DC-44~-59V) | 500 | 1700 | 180 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 500 | 150 | R134a | 60 |
CYDC106-1 | -48VDC(DC-44~-59V) | 600 | 2050 | 200 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 500 | 150 | R134a | 60 |
CYDC110-1 | -48VDC(DC-44~-59V) | 1000 | 3400 | 295 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 500 | 450 | R134a | 65 |
CYDC115-1 | -48VDC(DC-44~-59V) | 1500 | 5100 | 495 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 500 | 450 | R134a | 65 |
CYDC120-1 | -48VDC(DC-44~-59V) | 2000 | 6800 | 710 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 1000 | 700 | R134a | 69 |
CYDC130-1 | -48VDC(DC-44~-59V) | 3000 | 10200 | 1000 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 1000 | 900 | R134a | 69 |
CYDC140-1 | -48VDC(DC-44~-59V) | 4000 | 13650 | 1350 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 1000 | 1100 | R134a | 72 |
AC cabinet air conditioner (AC enclosure ac unit)
Model | Voltage | Nominal cooling capacity(W) (L35/L35) | Nominal cooling capacity(Btu/hr) (L35/L35) | Power consumption(W)(L35/L35) | IP Grade | Heater (W)(option) | Internal air flow (m3/h) | Refrigerant | Noise (dbA) |
CYAC103-2 | 220VAC | 300 | 1020 | 170 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 500 | 100 | R134a | 56 |
CYAC104-2 | 220VAC | 400 | 1360 | 215 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 500 | 110 | R134a | 56 |
CYAC105-2 | 220VAC | 500 | 1700 | 280 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 500 | 120 | R134a | 56 |
CYAC110-2 | 220VAC | 1000 | 3400 | 430 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 1000 | 230 | R134a | 62 |
CYAC112-2 | 220VAC | 1200 | 4080 | 498 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 1000 | 240 | R134a | 62 |
CYAC113-2 | 220VAC | 1300 | 4440 | 532 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 1000 | 260 | R134a | 63 |
CYAC115-2 | 220VAC | 1500 | 5100 | 600 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 1000 | 300 | R134a | 63 |
CYAC120-2 | 220VAC | 2000 | 6800 | 745 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 1000 | 500 | R134a | 63 |
CYAC125-2 | 220VAC | 2500 | 8500 | 846 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 2000 | 560 | R134a | 63 |
CYAC130-2 | 220VAC | 3000 | 10200 | 1240 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 2000 | 720 | R134a | 63 |
CYAC135-2 | 220VAC | 3500 | 11900 | 1360 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 2000 | 1250 | R134a | 63 |
CYAC150-2 | 220VAC | 5000 | 17000 | 2000 | IP55,NEMA 4, NEMA 4X | 2000 | 2300 | R134a | 63 |
Size and Design
The size and design of the unit should fit seamlessly into the existing setup. Compact and modular designs are often preferred for ease of installation and maintenance.
● Mounting method
Cabinet air conditioner design includes various mounting methods such as wall-mounting, semi-embedded mounting, and fully-embedded mounting, among others.
● Protection grade
The internal unit of a split household air conditioner has a low protection level, typically rated at IP30. While the outdoor unit offers rainproof functionality, outdoor cabinet air conditioners require a higher level of protection, generally rated at IP55, IP54, IP44, NEMA4 or NEMA4X, ensuring excellent waterproof performance.
● Anti-theft
The internal components of household air conditioners are made of engineering plastics, posing potential safety hazards. Additionally, the separation of the indoor and outdoor units leaves the outdoor unit exposed and vulnerable to theft. In contrast, cabinet air conditioners feature an integrated anti-theft design, making them impossible to remove from the outside once installed.
● Intelligent Monitoring and Remote Control
Household air conditioners typically use remote controls to turn the units on and off, lacking remote data transmission interfaces and only featuring high-voltage protection. In contrast, cabinet air conditioners (enclosure air conditioners) are equipped with comprehensive protection mechanisms, including high-voltage protection, evaporator icing protection, disconnection protection, overcurrent heat protection, high temperature alarms, and low temperature alarms. Additionally, an R-485 interface is installed to enable long-distance data transmission, centralized monitoring, and automatic alarms.
● Anti-Interference and Electromagnetic Compatibility
Engineered to endure robust electromagnetic environments, the cabinet air conditioner (cabinet cooling system) aligns with stringent EMC standards. This ensures it neither emits electromagnetic interference nor succumbs to shutdowns under intense electromagnetic conditions.
● Principal Components
■ Refrigerant
Typically, cabinet air conditioners employ R134a, an environmentally benign medium-pressure refrigerant. When ambient temperatures soar, R134a exhibits minimal cooling capacity degradation. Post-2016, the utilization of R22 refrigerant has been proscribed.
■ Fan
Industrial-grade fans, featuring self-lubricating ball bearings, are standard in cabinet air conditioners. These fans boast a remarkable operational lifespan of up to 80,000 hours, capable of continuous operation for a decade under 24-hour usage. Moreover, these fans possess waterproof attributes and high protection levels, conforming to IP54 or IP44 standards. They deliver extended air supply distances, substantial airflow volumes, and elevated air pressure.

Applications of Cabinet Air Conditioners (Cabinet AC Units)
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, cabinet air conditioners (cabinet ac units) are used to cool machinery control panels, motor control centers, and other critical equipment to prevent overheating and ensure smooth operations.
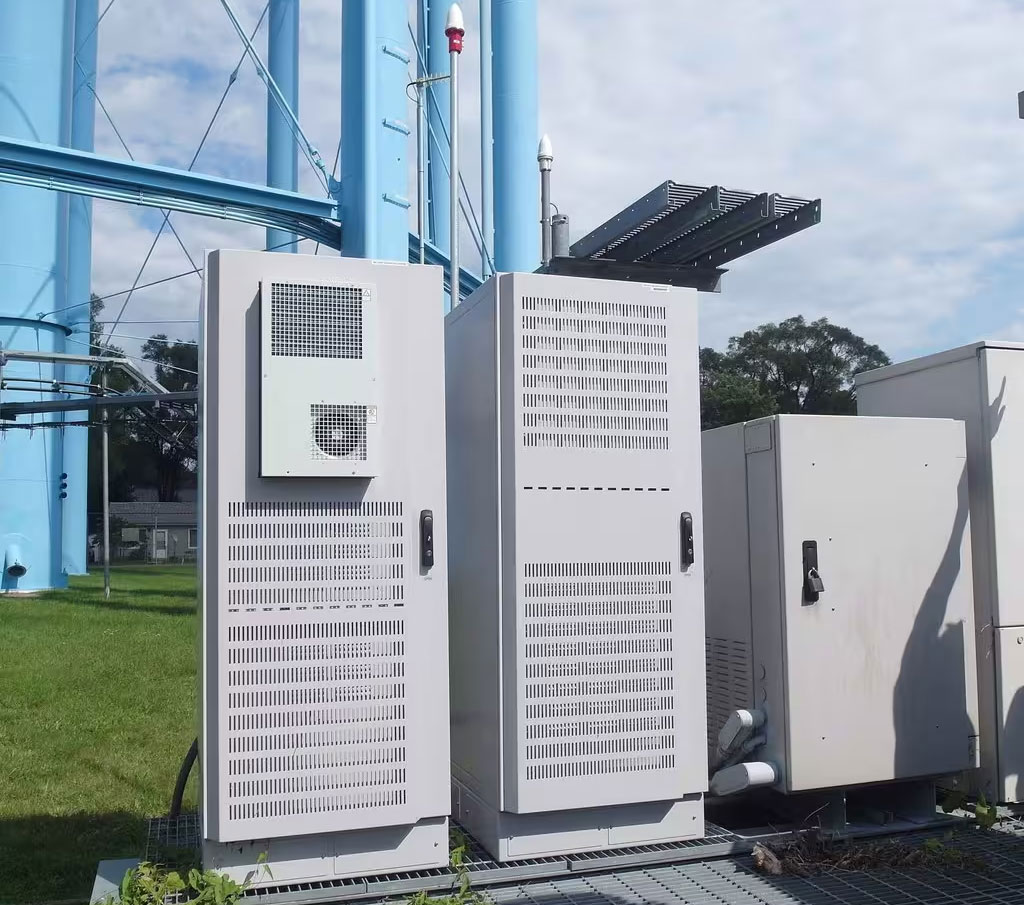

Commercial Applications
Commercial applications include cooling server racks, telecommunications equipment, and retail display cases, ensuring reliable performance and preventing downtime.
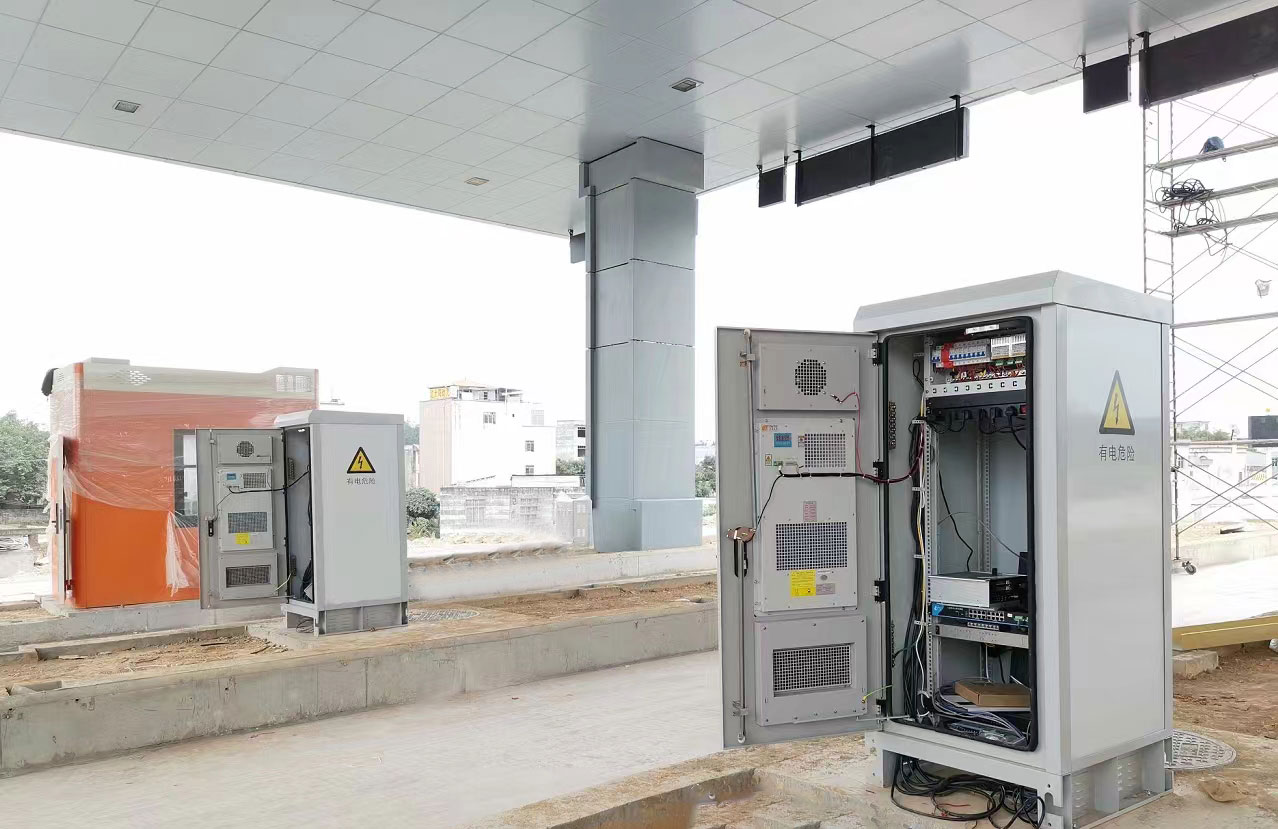

Residential Applications
While less common, cabinet air conditioners (cabinet cooling systems) can also be used in residential settings to cool home entertainment systems, computer workstations, and other electronic devices that generate heat.
Advantages of Using Cabinet Air Conditioners (Cabinet Air Conditioning Units)
Enhanced Equipment Performance
By maintaining a stable temperature, cabinet air conditioners (cabinet air conditioning units) enhance the performance and reliability of electronic components, reducing the risk of malfunctions and extending their lifespan.
Longevity of Electronic Components
Proper cooling prevents thermal stress on electronic components, ensuring they last longer and function more efficiently.
Energy Savings
Modern cabinet air conditioners are designed for energy efficiency, helping to reduce electricity costs while maintaining optimal cooling performance.
Space Efficiency
These units are specifically designed to fit within or on cabinets, making them a space-efficient solution for environments where space is at a premium.
Challenges and Considerations
Installation Challenges
Installing a cabinet air conditioner (cabinet type air conditioner) can be challenging, especially in tight or confined spaces. Proper planning and professional assistance may be required.
Maintenance Requirements
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the unit operates efficiently. This includes cleaning filters, inspecting components, and checking for refrigerant leaks.
Cost Considerations
While the initial cost can be high, the long-term benefits of energy savings and enhanced equipment performance often justify the investment.
Environmental Impact
It's important to consider the environmental impact, including the use of refrigerants that may contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing eco-friendly models can mitigate this issue.
Choosing the Right Cabinet Air Conditioner (Ac Cabinet)
Assessing Cooling Needs
Determine the cooling requirements based on the heat load generated by the equipment. This will help in selecting a unit with the appropriate cooling capacity.
Considering Space Constraints
Evaluate the available space for installation to ensure the chosen unit fits without obstructing other equipment.
Evaluating Energy Efficiency
Select a unit with high energy efficiency ratings to reduce operating costs and minimize environmental impact.
Budget Considerations
Consider the initial investment and ongoing operating costs to find a balance that meets your needs and budget.
Installation Process
Pre-Installation Checklist
Measure the installation space.
Ensure adequate ventilation.
Check electrical requirements.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Position the unit.
Secure the mounting brackets.
Connect the electrical supply.
Test the unit for proper operation.
Safety Tips During Installation
Follow manufacturer guidelines.
Use proper lifting techniques.
Ensure all electrical connections are secure.
Maintenance and Care
Regular Cleaning and Inspection
Keep filters and coils clean to maintain efficiency and prevent overheating. Regular inspections can identify issues before they become major problems.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues include insufficient cooling, unusual noises, and refrigerant leaks. Refer to the user manual or consult a professional for troubleshooting.
Professional Maintenance Services
Periodic professional maintenance can extend the life of the unit and ensure it operates at peak efficiency.

Innovations in Cabinet Air Conditioning (Cabinet Air Conditioning Units)
Smart Technology Integration
Modern units often feature smart technology, allowing remote monitoring and control via mobile devices or computers.
Advanced Cooling Technologies
Advancements such as variable speed compressors and improved refrigerants enhance performance and efficiency.
Eco-Friendly Developments
Newer models use eco-friendly refrigerants and energy-efficient components to reduce their environmental footprint.
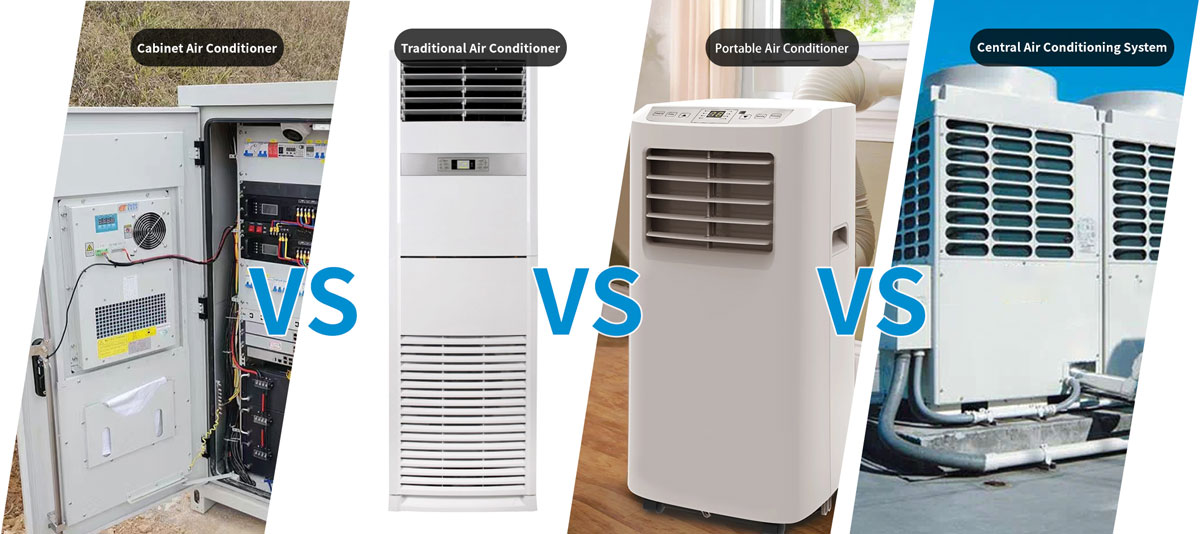
Comparing Cabinet Air Conditioners (Cabinet Air Conditioning Units ) to Other Cooling Systems
Cabinet Air Conditioners vs. Traditional Air Conditioners
Cabinet air conditioners (ac cabinets) or telecom cabinet air conditioner are designed for targeted cooling, whereas traditional air conditioners cool larger spaces. This makes cabinet units more efficient for specific applications.
Cabinet Air Conditioners vs. Portable Air Conditioners
Portable air conditioners are versatile but often less efficient for cooling enclosed spaces compared to cabinet air conditioners.
Cabinet Air Conditioners vs. Central Air Conditioning Systems
Central air systems are suitable for entire buildings, but cabinet air conditioners (cabinet ac units) provide precise cooling for individual enclosures, making them ideal for specialized applications.

Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Successful Implementations in Industries
Industries such as manufacturing and telecommunications have successfully implemented cabinet air conditioners to improve equipment reliability and performance.
Commercial Success Stories
Businesses like data centers and retail stores use these units to protect critical equipment and ensure continuous operation.
Residential Use Cases
Homeowners use cabinet air conditioners to cool high-performance computers and home entertainment systems, enhancing their lifespan and performance.
Top 10 Cabinet Air Conditioner Manufacturers Worldwide:
Schneider Electric (France)
Known for energy management and automation solutions, offering reliable cabinet cooling systems.
Rittal GmbH & Co. KG (Germany)
A global leader in enclosure and climate control technology for industrial applications.
Pfannenberg (Germany)
Specializes in thermal management, including cabinet air conditioners and cooling solutions.
Cytech Technology (China)
Offers innovative cabinet cooling systems designed for energy efficiency and reliability.
Delta Electronics (Taiwan)
Provides advanced cooling systems with a focus on sustainability and industrial applications.
Hammond Manufacturing (Canada)
Known for producing high-quality enclosure cooling solutions, including air conditioners.
Thermal Edge Inc. (USA)
Specializes in industrial cooling systems designed for harsh environments.
EIC Solutions, Inc. (USA)
Offers custom-designed cabinet air conditioning systems for various industries.
Kooltronic, Inc. (USA)
A leading provider of enclosure air conditioners and other thermal management products.
Daikin Industries, Ltd. (Japan)
Renowned for its HVAC expertise, including efficient cabinet cooling systems.
Future Trends in Cabinet Air Conditioning (Cabinet Cooling Solutions)
Predictive Maintenance
Future units may feature predictive maintenance capabilities, using sensors and AI to detect potential issues before they cause problems.
Increased Energy Efficiency
Ongoing advancements aim to improve energy efficiency, reducing both operating costs and environmental impact.
Integration with IoT
Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) will allow for more sophisticated monitoring and control, enhancing performance and convenience.
Conclusion
Cabinet air conditioners (cabinet ac units) or cabinet cooling solutions are indispensable in various settings, providing targeted cooling to ensure the optimal performance of critical equipment. From industrial applications to residential use, these units offer numerous benefits, including enhanced equipment longevity, energy savings, and space efficiency. By understanding the different types, features, and considerations, you can choose the right cabinet air conditioner to meet your specific needs.
FAQs
What is the lifespan of a cabinet air conditioner?
The lifespan of a cabinet air conditioner (ac outdoor unit cabinet) typically ranges from 10 to 15 years, depending on usage and maintenance.
Can cabinet air conditioners be used in residential settings?
Yes, cabinet air conditioners (cabinet ac units) can be used in residential settings to cool electronic devices and small enclosures.
How do I maintain my cabinet air conditioner?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning filters, inspecting coils, and checking for refrigerant leaks. Periodic professional servicing is also recommended.
Are cabinet air conditioners energy-efficient?
Modern cabinet air conditioners (cabinet ac units) are designed to be energy-efficient, with many models boasting high EER or SEER ratings.
What should I consider when buying a cabinet air conditioner?
Consider factors such as cooling capacity, energy efficiency, space constraints, and budget to select the best unit for your needs.





















