As communication networks and energy storage systems continue to expand, high-quality telecom cabinets and energy storage cabinets play a critical role in protecting core equipment and ensuring stable operation in outdoor and industrial environments.
To give you a clearer view of Cytech’s cabinet craftsmanship and design details, we have prepared a product video showcasing key structural and internal features.
1. The Importance of Telecom Cabinets &Energy Storage Cabinets and Why Failures Occur
Telecom cabinets and energy storage cabinets (ESS cabinets) are far more than simple enclosures — they serve as the backbone of network reliability and battery energy storage system stability in industrial and outdoor enclosures.
A telecom cabinet protects switches, optical modules, and transmission boards, ensuring uninterrupted network signal transmission and reducing telecom equipment downtime.
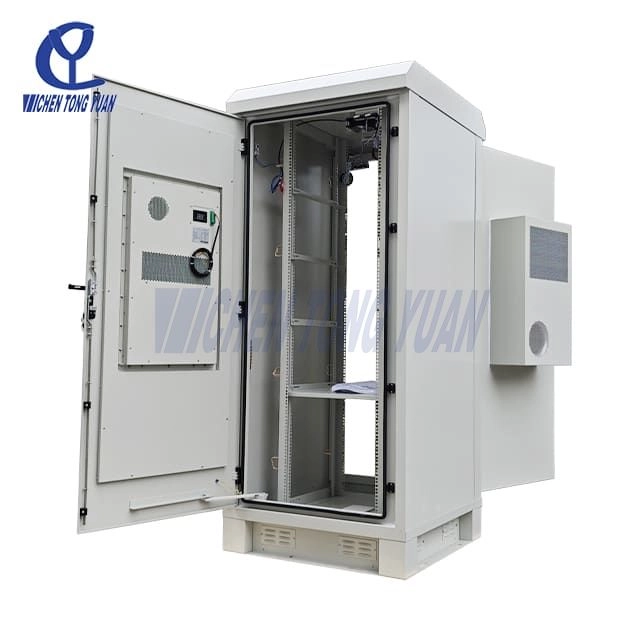

Energy storage cabinets safeguard batteries, PCS, and BMS systems, maintaining cells within safe temperature ranges and preventing battery short circuits, thermal runaway, and overheating hazards in BESS enclosures.
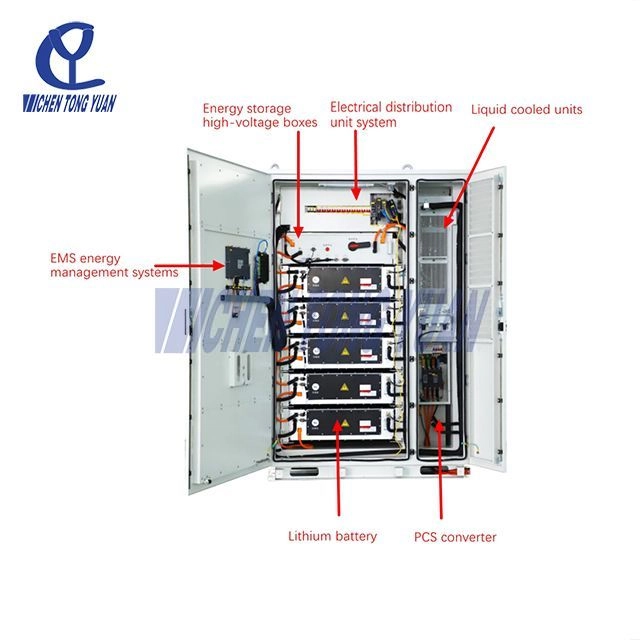

Despite their robust design, these cabinets often face high failure rates. Harsh outdoor conditions, including extreme ambient temperatures, high humidity, dust, and UV exposure in outdoor enclosures, exert significant stress on industrial cabinet materials.
Internally, high equipment heat, inadequate cooling systems for telecom cabinets and ESS cabinets, improper layout, and messy wiring exacerbate the problem. Furthermore, irregular maintenance or delayed inspections often allow small issues to escalate into major failures.
To provide practical guidance, the following sections detail the five most common failures of telecom and energy storage cabinets by Cytech, offering step-by-step diagnostic and resolution methods.
2. Top 5 Common Telecom Cabinet Failures and Analysis

| Top 5 Common Telecom Cabinet Failures — QuickSummary Table |
| Failure Type | Key Issues | Main Causes | Quick Solutions (Essentials) |
| 1. Poor Cooling Leading to Overheating | Alarms triggered, loud fans, dropped connections, auto-reboots, multiple components overheating | Insufficient cooling capacity, poor airflow design, overcrowded equipment, clogged filters | ·Check temperature logs
· Verify cooling capacity
· Improve airflow
· Rearrange equipment
· Clean/replace filters
· Add temporary cooling
· Upgrade cooling system |
| 2. High Humidity Causing Moisture Inside | Condensation, oxidized ports, optical module issues, short circuits, corrosion | High external humidity, worn door seals, faulty/no dehumidification | ·Check humidity sensors
· Inspect seals
· Verify AC/dehumidification
· Confirm IP rating
· Use silica gel temporarily
· Replace seals/upgrade cabinet/add dehumidifier |
| 3. Dust Accumulation Causing Equipment Faults | Fan clogging, poor heat dissipation, PCB dust buildup, shutdowns or short circuits | Dusty environment, poor filtration, infrequent maintenance | ·Check internal dust
· Clean/replace filters
· Install better filters
· Regular maintenance
· Use heat exchangers in dusty areas |
4. Equipment Vibration Causing Port Contact Issues | Intermittent connection, unstable signals, frequent port errors | Uneven installation, loose equipment, external vibrations | · Level the cabinet
· Secure devices
· Tighten connectors
· Reorganize wiring
· Monitor stability |
5. Power and Wiring Abnormalities | Voltage fluctuations, module reboots, partial/total outages | Improper wiring, loose terminals, poor grounding | ·Inspect wiring layout
· Tighten terminals
· Verify grounding
· Add surge/voltage protection · Monitor after fixes |
2.1Poor Cooling Leading to Overheating in Outdoor Telecom Cabinets
2.1.1 Issues
Overheating can manifest in several ways: equipment alarms frequently trigger, fans become unusually loud, network connections drop intermittently, and devices may reboot automatically. Overheating often affects multiple components simultaneously, creating a ripple effect that compromises overall telecom cabinet performance.
2.1.2 Causes
Insufficient cooling systems for telecom cabinets
Inadequate airflow design in outdoor telecom enclosures, resulting in hot spots
Overcrowded internal equipment
Clogged or dirty high-efficiency air filters
2.1.3 Solutions (Step-by-Step Guide)
Check Temperature Alerts: Review AC and device temperature logs to pinpoint peak heat periods.
Verify Cooling Capacity: Ensure the installed AC or heat exchanger meets the total load of all internal devices.
Inspect Airflow Design: Confirm that airflow paths are clear and no dead zones prevent proper ventilation.
Check Equipment Layout: Rearrange equipment to prevent stacking that creates heat accumulation.
Inspect Filters and Fans: Clean or replace high-efficiency filters, ensure fans operate at full capacity.
Temporary Measures: Deploy auxiliary fans, apply shading, or reduce non-essential device load to lower temperatures quickly.
Long-Term Solutions: Upgrade telecom cooling systems, optimize internal airflow, and implement proper device spacing to maintain consistent heat dissipation.
2. 2High Humidity Causing Moisture Inside Communication Cabinets
2.2.1 Issues
Moisture-related issues may include oxidized ports, malfunctioning optical modules, short circuits, and condensation forming on cabinet walls. Long-term exposure can cause corrosion of metal components and degradation of insulation, ultimately shortening telecom equipment lifespan.
2.2.2 Causes
Persistent high external humidity
Aging or damaged door seals
Malfunctioning or absent dehumidification systems for telecom cabinets
2.2.3 Solutions (Step-by-Step Guide)
Monitor Humidity Sensors: Check internal sensors or alerts to locate areas affected by moisture intrusion in telecom cabinets.
Inspect Door Seals: Look for cracks, wear, or compression loss that could compromise sealing.
Verify Dehumidification System: Ensure AC units or heat exchangers are functioning properly with adequate airflow.
Confirm IP Rating: Verify that the cabinet’s IP rating is appropriate for the environment; upgrade if necessary.
Temporary Mitigation: Use silica gel packs or localized heating to reduce immediate moisture.
Implement Long-Term Fixes: Replace seals, upgrade cabinet rating, or add dedicated dehumidification solutions.
2.3Dust Accumulation Causing Equipment Faults in Outdoor Telecom Enclosures
2.3.1 Issues
Dust can clog fans, impede heat dissipation, coat PCBs, and increase overall failure rates. In severe cases, accumulated dust may cause short circuits or trigger unexpected shutdowns in outdoor telecom enclosures.
2.3.2 Causes
Dusty outdoor environments
Fans drawing in dust due to inadequate filtration
Infrequent maintenance and cleaning
2.3.3 Solutions (Step-by-Step Guide)
Inspect Internal Surfaces: Check for visible dust on PCBs, fans, and air intakes.
Examine Filters: Remove and assess filter condition; clean or replace if clogged.
Install High-Efficiency Filters: Upgrade to finer filters or dust-proof screens where necessary.
Schedule Regular Maintenance: Establish a monthly cleaning routine.
Consider Heat Exchangers: In high-dust environments, use heat exchangers for telecom cabinets instead of fan-driven airflow.
2. 4 Equipment Vibration Causing Port Contact Issues in Telecom Cabinets
2.4.1 Issues
Intermittent network connections, unstable signals, and frequent port errors are common when equipment vibrates excessively.
2.4.2 Causes
Uneven cabinet installation
Equipment not secured properly
Environmental or transport vibrations
2.4.3 Solutions (Step-by-Step Guide)
Check Cabinet Level: Use a spirit level to ensure the base is even.
Secure Equipment: Add brackets, rails, or mounting hardware to fix devices in place.
Inspect Wiring and Terminals: Reorganize loose cables and tighten connectors.
Monitor After Adjustments: Confirm stability over several operating cycles.
2.5 Power and Wiring Abnormalities in Communication Cabinets
2.5.1 Issues
Issues include voltage fluctuations, module reboots, or complete power outages, often affecting multiple subsystems.
2.5.2 Causes
Messy or improper wiring
Loose terminals
Incomplete grounding
2.5.3 Solutions (Step-by-Step Guide)
Inspect Wiring Layout: Look for tangled or crossed cables that may cause intermittent issues in telecom and ESS cabinets.
Check Terminal Connections: Tighten loose connectors and verify correct termination.
Test Grounding: Ensure all components are properly grounded according to standards.
Install Protective Devices: Add surge protectors or voltage stabilizers on key circuits.
Monitor System Response: Verify stability after corrections and ensure no repeat faults.
3. Top 5 Common Energy Storage Cabinet Failures and Analysis
| Top 5 Common Energy Storage Cabinet Failures — Quick Summary Table |
| Failure Type | Key Issues | Main Causes | Quick Solutions (Essentials) |
1. Abnormal Battery
Temperature Rise | High battery temperature alarms,
reduced lifespan,
lower charging/discharging efficiency | Insufficient cooling,
poor airflow design,
modules stacked too closely | ·Check BMS temperature logs
· Inspect cooling capacity of AC/fans
· Verify unobstructed airflow paths
· Adjust battery module spacing for ventilation
· Monitor temperature stability over several charge/discharge cycles |
2. Moisture Intrusion
Causing Short Circuits | Corroded terminals,
reduced insulation,
system trips,
sudden shutdowns | Damaged door seals,
low IP rating,
poor waterproofing at openings | ·Inspect door seals for cracks/wear
· Confirm cabinet IP rating meets outdoor conditions
· Check waterproof connectors/covers
· Use moisture absorbers or localized heating temporarily
· Replace seals and improve waterproofing; upgrade cabinet/add dehumidification |
3. Poor Electrical
Wiring Layout | Loose connections,
arcing,
unstable operation,
potential electric shock hazards | Messy wiring layout,
unmarked terminals,
incomplete grounding | ·Reorganize wiring using trays/ties
· Label all terminals clearly
· Verify grounding continuity and compliance
· Test overall system stability after corrections |
| 4. BMS/PCS Telecom Failures | Alarms triggered,
data upload failures,
system stops responding | Loose cables,
electromagnetic interference,
incorrect telecom protocol settings | ·Tighten and check all telecom cables
· Use shielded cables to reduce EMI
· Verify BMS/PCS protocol configurations
· Monitor data transmission stability after adjustments |
| 5. Fan or AC System Failure | Battery/module overheating,
repeated temperature alarms | Cooling device malfunction,
blocked filters,
insufficient AC cooling capacity | · Check operation of fans/AC unit
· Clean clogged filters
· Verify cooling capacity vs heat load
·Monitor temperature performance after maintenance |
3. 1 Abnormal Battery Temperature Rise in Energy Storage Cabinets
3.1.1 Issues
High battery temperatures trigger BMS or PCS alarms, reduce battery lifespan, and decrease charging/discharging efficiency in energy storage cabinets (ESS cabinets).
3.1.2 Causes
3.1.3 Solutions (Step-by-Step Guide)
Check Temperature Logs: Review BMS records for temperature spikes and trends.
Inspect Cooling System: Ensure AC or fan-based battery cooling systems meet required capacity.
Verify Airflow: Make sure airflow paths are unobstructed and heat is evenly dissipated.
Check Battery Arrangement: Avoid stacking modules too closely; allow space for ventilation.
Monitor After Adjustments: Confirm temperature stability over several cycles.
3.2 Moisture Intrusion Causing Short Circuits in Battery Storage Enclosures
3.2.1 Issues
Corroded terminals, reduced insulation, system trips, or unexpected shutdowns in battery storage enclosures.
3.2.2 Causes
Door seals degraded or damaged
Cabinet IP rating too low
Improper waterproofing of openings
3.2.3 Solutions (Step-by-Step Guide)
Inspect Seals: Check for cracks or wear on door seals.
Check IP Rating: Ensure cabinet is suitable for environmental conditions; upgrade if necessary.
Examine Openings: Verify waterproof connectors and covers are installed correctly.
Apply Temporary Measures: Use moisture absorbers or local heating to reduce immediate risk.
Implement Long-Term Fixes: Replace seals, upgrade cabinet, or add dedicated dehumidification for ESS cabinets.
3.3 Poor Electrical Wiring Layout in ESS Cabinets
3.3.1 Issues
Loose connections, arcs, unstable operation, or electric shock hazards.
3.3.2 Causes
Messy wiring
Unmarked terminals
Incomplete grounding
3.3.3 Solutions (Step-by-Step Guide)
Organize Wiring: Use cable trays and zip ties to route wires neatly in ESS cabinets.
Mark Terminals: Ensure all connections are clearly labeled.
Check Grounding: Confirm all components meet grounding standards.
Test Operation: Verify system stability after corrections.
3.4 BMS/PCS telecom Failures in Energy Storage Cabinets
3.4.1 Issues
Alarms triggered, data not uploaded, system stops working.
3.4.2 Causes
3.4.3 Solutions (Step-by-Step Guide)
Check Connections: Ensure all cables are tightly connected.
Use Shielded Cables: Reduce interference.
Verify Protocol Settings: Confirm BMS and PCS configurations match system requirements.
Monitor Telecoms: Test data transmission stability in battery storage enclosures.
3.5 Fan or AC System Failure in Energy Storage Cabinets
3.5.1 Issues
Battery or module overheating, triggering alarms.
3.5.2 Causes
3.5.3 Solutions (Step-by-Step Guide)
Inspect Cooling Device: Check operation of AC or fans in ESS cabinets.
Clean Filters: Remove dust and debris.
Verify Cooling Capacity: Ensure unit matches heat load requirements.
Monitor Temperature: Confirm stability post-maintenance.
4. 5 Practical Tips to Reduce Telecom Cabinets and Energy Storage Cabinets Failures
4.1 Proper Cooling System Selection for Telecom Cabinets and ESS Enclosures
Select AC, heat exchangers, or fan combinations based on total equipment power, ambient temperature, and extreme conditions. Ensure cooling systems for telecom cabinets and ESS cabinets meet peak load and leave margin for future expansion.
4.2 Choose Appropriate IP Rating for Outdoor Telecom and Energy Storage Cabinets
Outdoor cabinets must match environmental conditions. Higher IP ratings for telecom cabinets and energy storage cabinets prevent dust, water, and corrosion ingress, reducing moisture and dust-induced failures.
4.3 Optimize Internal Layout and Airflow in Communication Cabinets and Battery Storage Cabinets
Arrange devices to minimize hot spots. Partition power modules, batteries, and control units. Keep airflow channels clear to enhance cooling efficiency in telecom cabinets and battery storage enclosures.
4.4 Establish Regular Maintenance Schedule for Telecom and ESS Cabinets
Include filter cleaning, AC checks, seal inspection, terminal verification, and cable tightening. Routine maintenance identifies small issues before they escalate in telecom and energy storage cabinets.
4.5 Choose Reliable Supplier and Complete Solutions for Custom Telecom Cabinets and Energy Storage Solutions (Cytech)
A reputable supplier provides cabinets, cooling, sealing, wiring, and long-term technical support. Cytech offers professional solutions, custom telecom cabinets, and energy storage solutions, with hands-on guidance to solve real-world issues.
5. Conclusion
Telecom and energy storage cabinets are critical for equipment protection, temperature control, electrical safety, and system reliability. Most failures stem from poor cooling, moisture, messy wiring, or lack of maintenance. Proper design, optimized layout, regular inspection, and collaboration with a reliable supplier like Cytech can prevent most problems.
If your cabinets are already experiencing overheating, moisture, repeated faults, or wiring issues, Cytech provides professional telecom cabinets, energy storage cabinets, cooling solutions, and custom services to ensure safe, stable operation.















