Outline
1. What are IP Ratings?
2. How IP Ratings are Structured
3. Overview of IP55 Rating
4. Overview of IP65 Rating
5. Key Differences Between IP55 and IP65
6. Common Applications of IP55
7. Common Applications of IP65
8. Practical Scenarios for Choosing IP55 Over IP65
9. Practical Scenarios for Choosing IP65 Over IP55
10. Cost Implications of IP55 and IP65 Ratings
11. Durability and Maintenance Considerations
12. Industry Standards and Testing for IP Ratings
13. Choosing the Right IP Rating for Your Needs
14. How to Interpret Other IP Ratings (IP67, IP68, etc.)
15. FAQs about IP55 and IP65 Ratings
16. Conclusion
Introduction
In today's world, technological devices and electrical enclosures face diverse environmental conditions, from dust and debris to rain and water exposure. Whether you're selecting outdoor equipment or industrial machinery, understanding the protection offered by Ingress Protection (IP) ratings is crucial. Two common ratings, IP55 and IP65, offer varying degrees of protection against solids and liquids. In this article, we'll dive into the differences between these ratings and help you choose the right one for your needs.
What are IP Ratings?
IP ratings, or Ingress Protection ratings, are defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) under the standard IEC 60529. They classify the degree of protection provided by mechanical casings and electrical enclosures against the intrusion of solid objects like dust and water. The two-digit code following the letters "IP" indicates the specific level of protection offered.

Why are IP Ratings Important?
● They help consumers and manufacturers understand the durability and reliability of a product.
● IP ratings ensure that products can withstand specific environmental factors.
● Industries such as electronics, construction, and automotive rely on IP ratings to certify the safety and longevity of their equipment.
How IP Ratings are Structured
IP ratings consist of two digits. The first digit denotes the protection level against solids (like dust or debris), while the second digit represents protection against liquids (such as rain or water jets).
First Digit: Protection Against Solid Objects
● 0: No protection against solid objects.
● 1: Protection against objects larger than 50mm.
● 2: Protection against objects larger than 12.5mm.
● 3: Protection against objects larger than 2.5mm.
● 4: Protection against objects larger than 1mm.
● 5: Limited protection against dust (some ingress is tolerated).
● 6: Complete protection against dust (dust-tight).
Second Digit: Protection Against Liquids
● 0: No protection.
● 1: Protection against dripping water.
● 2: Protection against dripping water when tilted up to 15°.
● 3: Protection against water spray.
● 4: Protection against splashing water.
● 5: Protection against water jets.
● 6: Protection against powerful water jets.
● 7: Protection against temporary immersion in water.
● 8: Protection against continuous immersion in water.
Overview of IP55 Rating
An IP55 rating indicates that the product is moderately protected against dust and can withstand low-pressure water jets from any direction. Here's a breakdown of its capabilities:
Solid object protection (5): Some dust ingress is allowed, but it does not interfere with the operation of the equipment.
Water protection (5): The enclosure can resist water jets from a 6.3mm nozzle, coming from any direction, without harmful effects.
Best Use Cases for IP55:
● Outdoor lighting
● Telecommunication equipment
● Industrial machinery
General-purpose enclosures that face moderate weather conditions

Overview of IP65 Rating
The IP65 rating is a significant upgrade in terms of protection. This rating ensures that the product is completely dust-tight and can also resist low-pressure water jets. Here’s the breakdown:
● Solid object protection (6): Complete protection against dust. The enclosure is fully sealed to prevent any dust ingress.
● Water protection (5): Like IP55, IP65-rated equipment can withstand water jets from any direction, but it offers better overall environmental resistance.
Best Use Cases for IP65:
● Outdoor and industrial lighting fixtures
● Marine electronics
● Heavy machinery and outdoor equipment used in extreme weather conditions
● Electrical boxes and junctions in construction sites

Key Differences Between IP55 and IP65
1. Dust Protection:
● IP55 offers partial protection against dust, meaning some dust ingress is allowed but not enough to affect performance.
● IP65, on the other hand, provides complete protection from dust.
2. Water Resistance:
● Both IP55 and IP65 can resist water jets, but the level of sealing is superior in IP65-rated products, making them more suitable for harsher outdoor environments.
3. Durability in Harsh Environments:
● IP65 devices are better suited for environments where complete dust exclusion is necessary, such as in desert or construction settings, while IP55 is suitable for less extreme conditions.

Common Applications of IP55
IP55-rated devices are ideal for environments with moderate dust and water exposure. Some of the common applications include:
● Outdoor lighting: IP55-rated outdoor lights can withstand weather conditions such as light rain and dust.
● Ventilation systems: These systems are often rated IP55 to handle environments with airborne particles while maintaining functionality.
● Telecommunication and networking equipment: Outdoor telecom boxes frequently use IP55 enclosures to protect against environmental exposure.

Outdoor lighting
Ventilation systems

Telecommunication and networking equipment
Common Applications of IP65
IP65-rated devices are designed for more demanding environments, where both dust and water pose significant risks. Some typical applications are:
● Industrial equipment: Machines that operate in outdoor environments, such as construction sites or agricultural fields, require IP65-rated enclosures to protect sensitive electronics.
● Marine applications: IP65 is common for equipment used on ships or near water bodies, as it provides robust protection against splashing water and dust.
● Heavy outdoor lighting: Floodlights and spotlights in stadiums or commercial settings often have IP65 ratings to ensure reliable performance under harsh weather conditions.

Industrial equipment
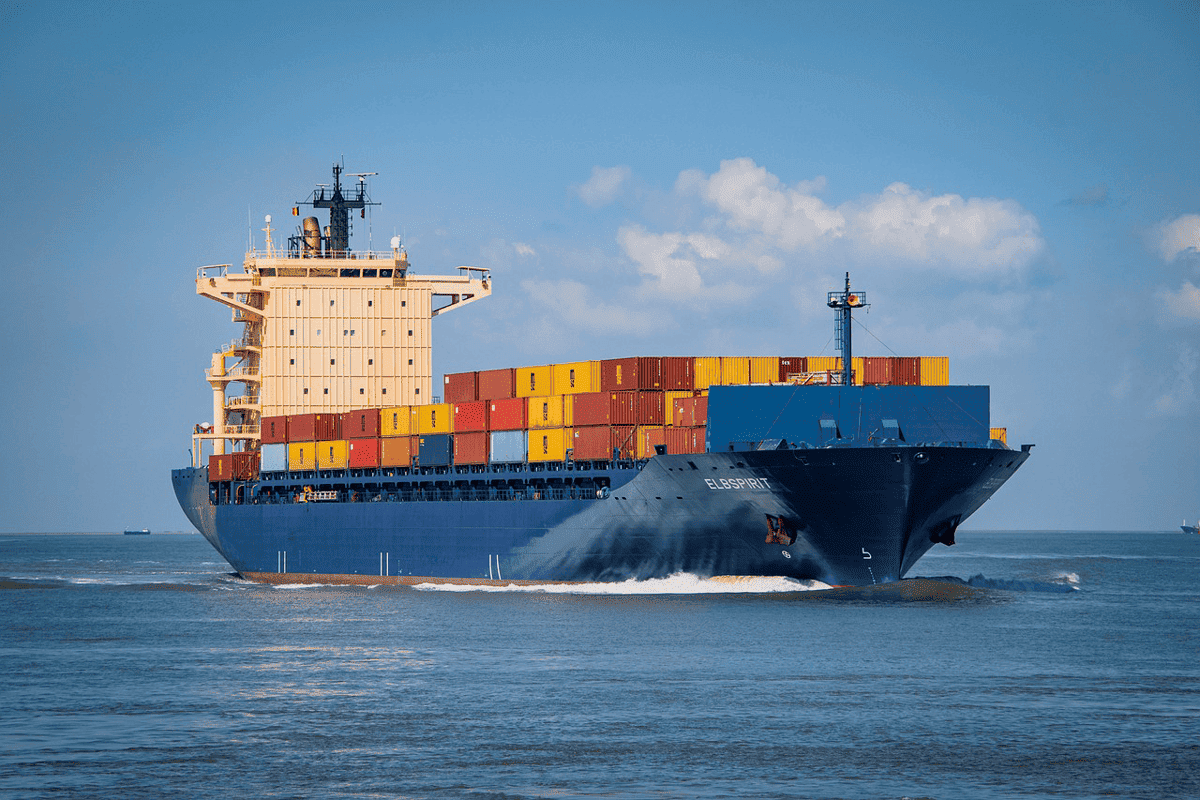

Marine applications
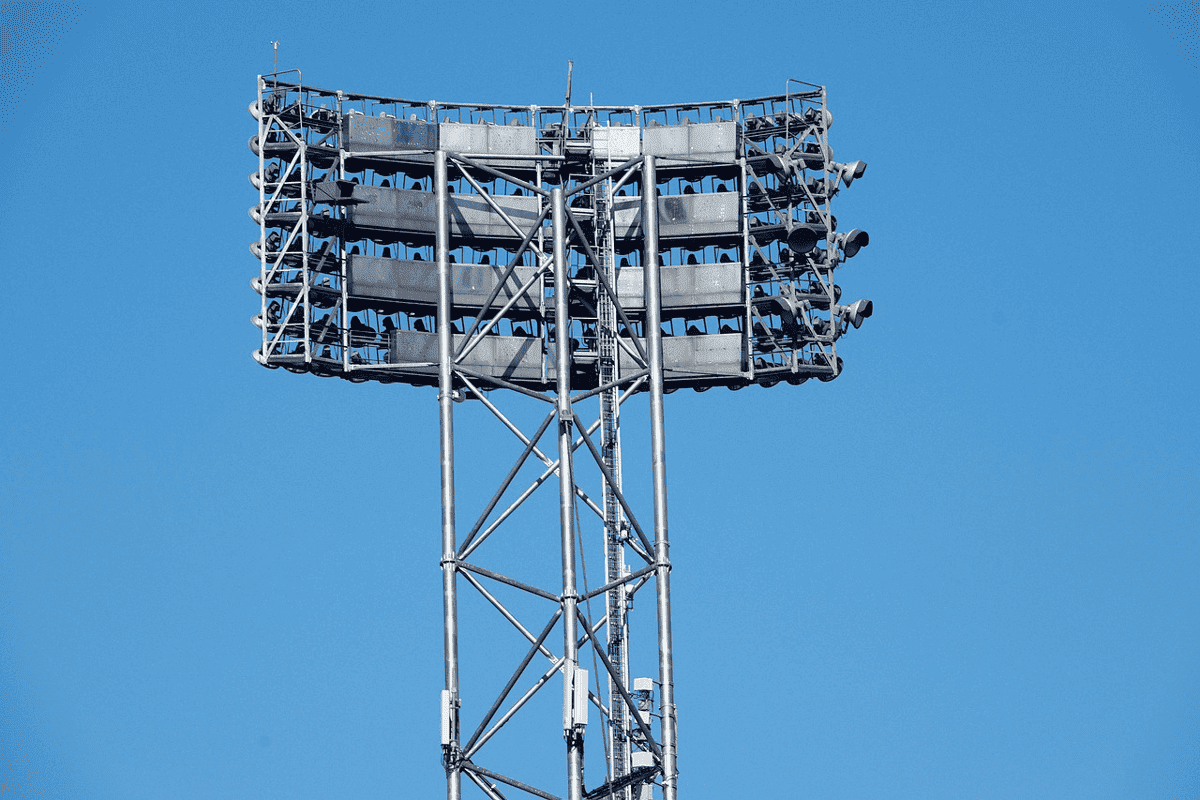

Heavy outdoor lighting
Practical Scenarios for Choosing IP55 Over IP65
There are specific scenarios where an IP55 rating is more than adequate, such as:
● Indoor or sheltered outdoor use: If a device is placed under a shelter but exposed to some dust and occasional light rain, IP55 provides sufficient protection.
● Cost-sensitive projects: In situations where extreme dust or water protection isn't necessary, IP55 is often more affordable than IP65-rated products.
Practical Scenarios for Choosing IP65 Over IP55
On the other hand, IP65 is crucial for environments that demand high levels of protection:
● Construction sites: These environments are often filled with dust, and heavy rain is common. IP65 is ideal for protecting equipment in such harsh conditions.
● Outdoor installations in desert climates: The complete dust protection of IP65 is critical in dusty environments like deserts, where equipment could otherwise fail due to dust ingress.
Cost Implications of IP55 and IP65 Ratings
Generally, IP65-rated equipment tends to be more expensive than IP55-rated counterparts. The higher cost is due to the enhanced sealing mechanisms and materials used to ensure complete protection against dust and water. While IP65 offers superior protection, it's important to weigh this against the actual environmental risks and budget constraints when choosing between IP55 and IP65.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
● IP55: Devices with this rating may require more frequent cleaning and inspection, especially in environments with higher dust levels.
● IP65: Equipment rated IP65 is more resilient and requires less frequent maintenance, making it a better choice for long-term use in demanding conditions.
Industry Standards and Testing for IP Ratings
IP ratings are governed by the IEC 60529 standard, which outlines the procedures for testing the protection levels of enclosures against dust and water. Manufacturers must undergo rigorous testing to ensure compliance, and third-party verification is often required for certification.
Choosing the Right IP Rating for Your Needs
Selecting the right IP rating depends on several factors, including the level of dust, water exposure, and the environment in which the equipment will operate. For general-purpose outdoor use, IP55 may be sufficient, but for environments with heavy dust or water exposure, IP65 is a better option.
Cytech's IP 55 Outdoor Cabinet and IP 65 Outdoor Cabinet
How to Interpret Other IP Ratings (IP67, IP68, etc.)
While IP55 and IP65 are common, other ratings such as IP67 and IP68 offer even greater protection. For instance, IP67-rated devices can withstand full immersion in water for up to 30 minutes, and IP68 can handle prolonged submersion. These are necessary for specific applications, such as underwater lighting or equipment exposed to frequent submersion.
FAQs about IP55 and IP65 Ratings
1. Can IP55 devices be used outdoors?
Yes, IP55 devices are suitable for outdoor use, especially in areas with moderate weather conditions.
2. Is IP65 completely waterproof?
No, IP65 is not fully waterproof, but it offers protection against water jets, making it suitable for outdoor and wet environments.
3. What does the "5" in IP55 stand for?
The "5" in IP55 stands for protection against limited dust ingress and low-pressure water jets.
4. Are IP65 devices more expensive than IP55?
Yes, generally IP65-rated devices are more expensive due to their enhanced protection levels.
5. Can IP55-rated products be submerged in water?
No, IP55 products are not designed for submersion. They can resist water jets but not immersion.
6. What are the limitations of IP65?
While IP65 offers excellent protection against dust and water jets, it is not suitable for continuous immersion in water.
Conclusion
Choosing between IP55 and IP65 depends on the specific environmental challenges your equipment will face. IP55 offers sufficient protection for moderately dusty and wet environments, while IP65 is designed for harsher conditions. Consider the level of dust and water exposure in your environment, as well as budget constraints, when making your decision.























