In today’s industries, efficiency and reliability are the key drivers of success. Electrical and electronic equipment such as PLCs, drives, telecommunication systems, and energy storage units form the backbone of many modern operations. Yet, these sophisticated systems face a common and potentially damaging problem: excessive heat inside cabinets and enclosures. If not controlled, overheating can shorten equipment lifespan, cause system failures, and result in costly downtime
One of the most effective solutions available today is the air to air cabinet heat exchanger. In this detailed guide, we will explore what cabinet heat exchangers are, how they work, their benefits, applications across industries, and why they are a smart investment for businesses.
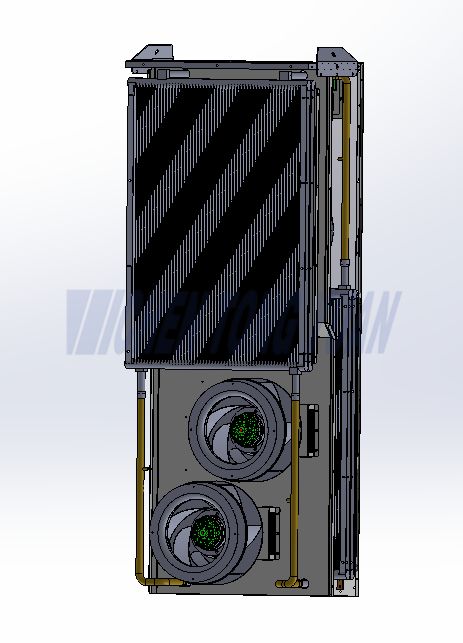
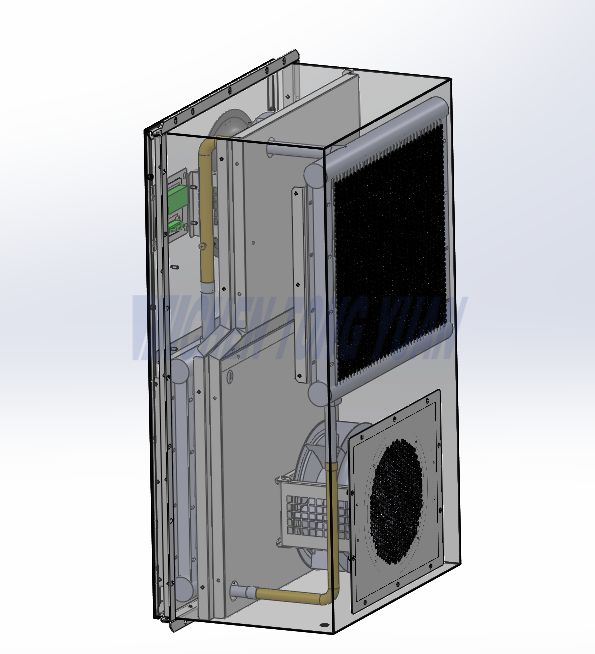
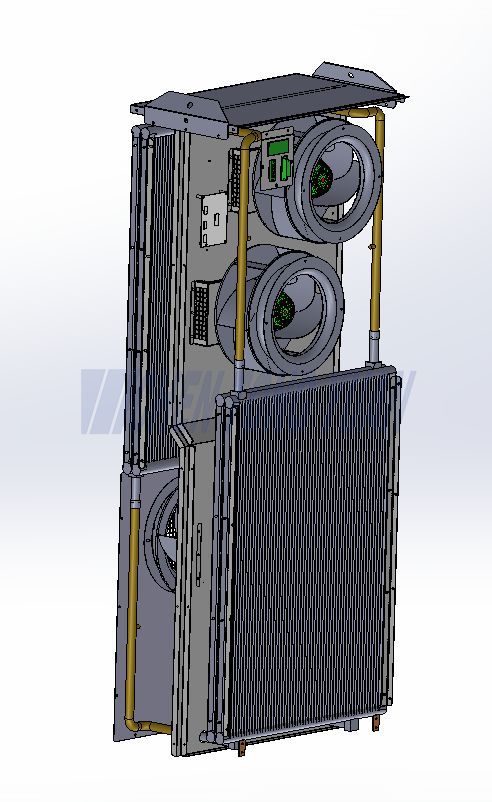
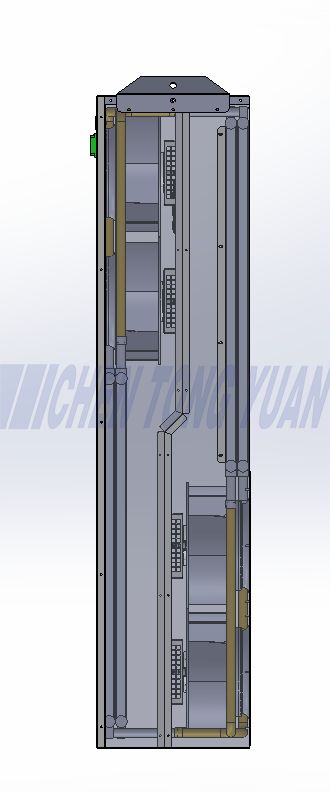

What is an air to air Cabinet Heat Exchanger?
◆Concept of HEX
A cabinet heat exchanger (HEX) is a thermal management device designed to remove unwanted heat from inside an electrical enclosure and release it into the surrounding environment. Unlike air conditioners that rely on refrigerants or simple fans that circulate air, heat exchangers transfer heat using advanced thermal
and convection methods.
◆Types of cabinet heat exchangers:
Type 1 :Air-to-Air Plate Heat Exchangers
Core Concept
A Plate Heat Exchanger (PHE) is a type of heat exchanger that uses metal plates to transfer heat between cold air and hot air. It is a highly efficient and compact device where the cold air and hot air are separated by the plates, preventing them from mixing while allowing heat to pass through.
When there is a large temperature difference, the device will effectively exchange heat between hot air inside and cool air outside the cabinet through the aisle of multilayer aluminum heat sink fins, which makes the cabinet be an enclosed system with constant temperature so that equipment inside the cabinet can work normally.
Imagine it as a stack of metal plates, like the pages of a book, with channels between them. A hot air flows through every other channel, and a cold air flows through the channels in between. The heat from the hot air transfers through the thin metal plates to warm up the cold air.
Air to Air Heat Exchanger Core(Key Components)
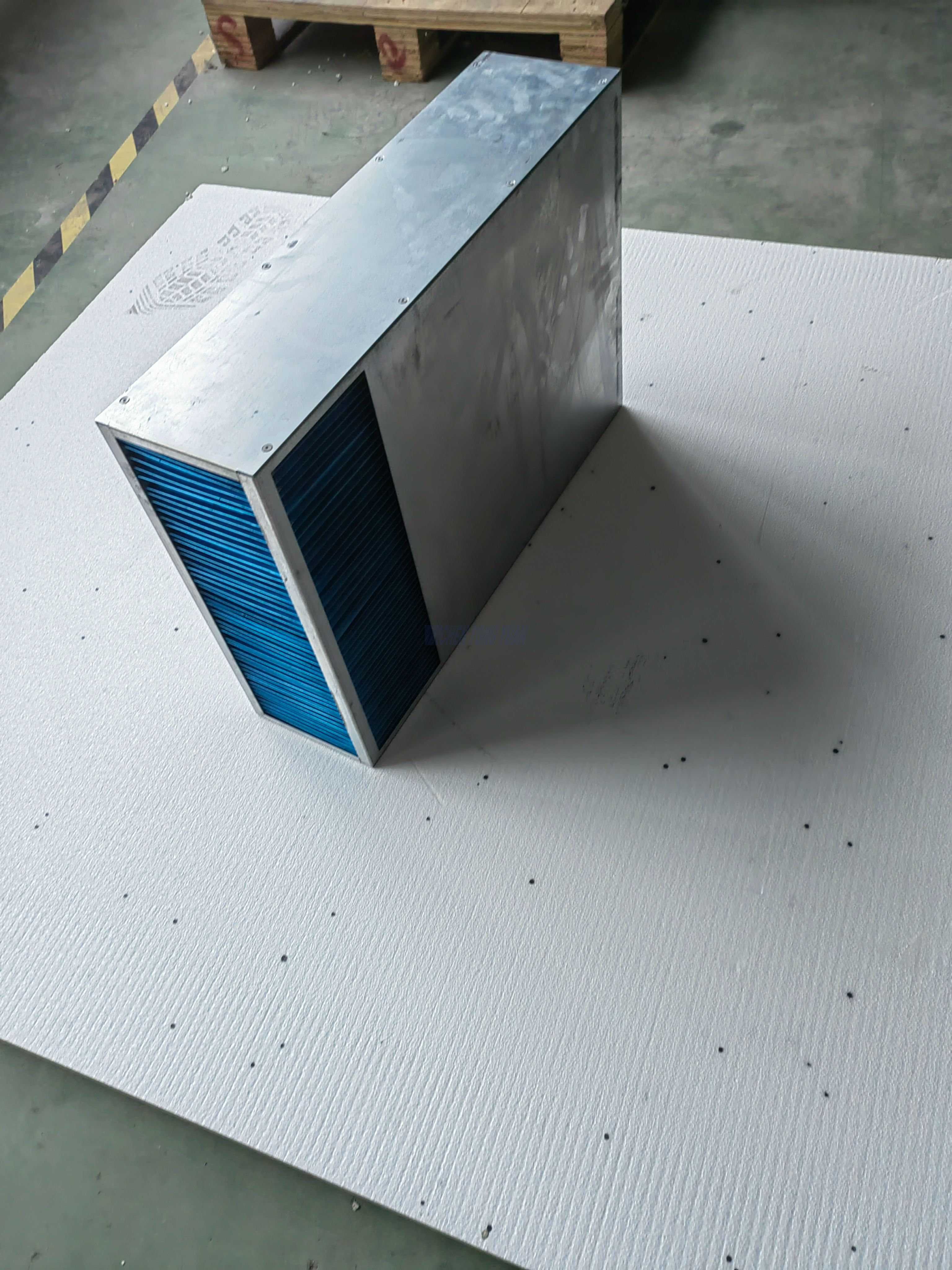

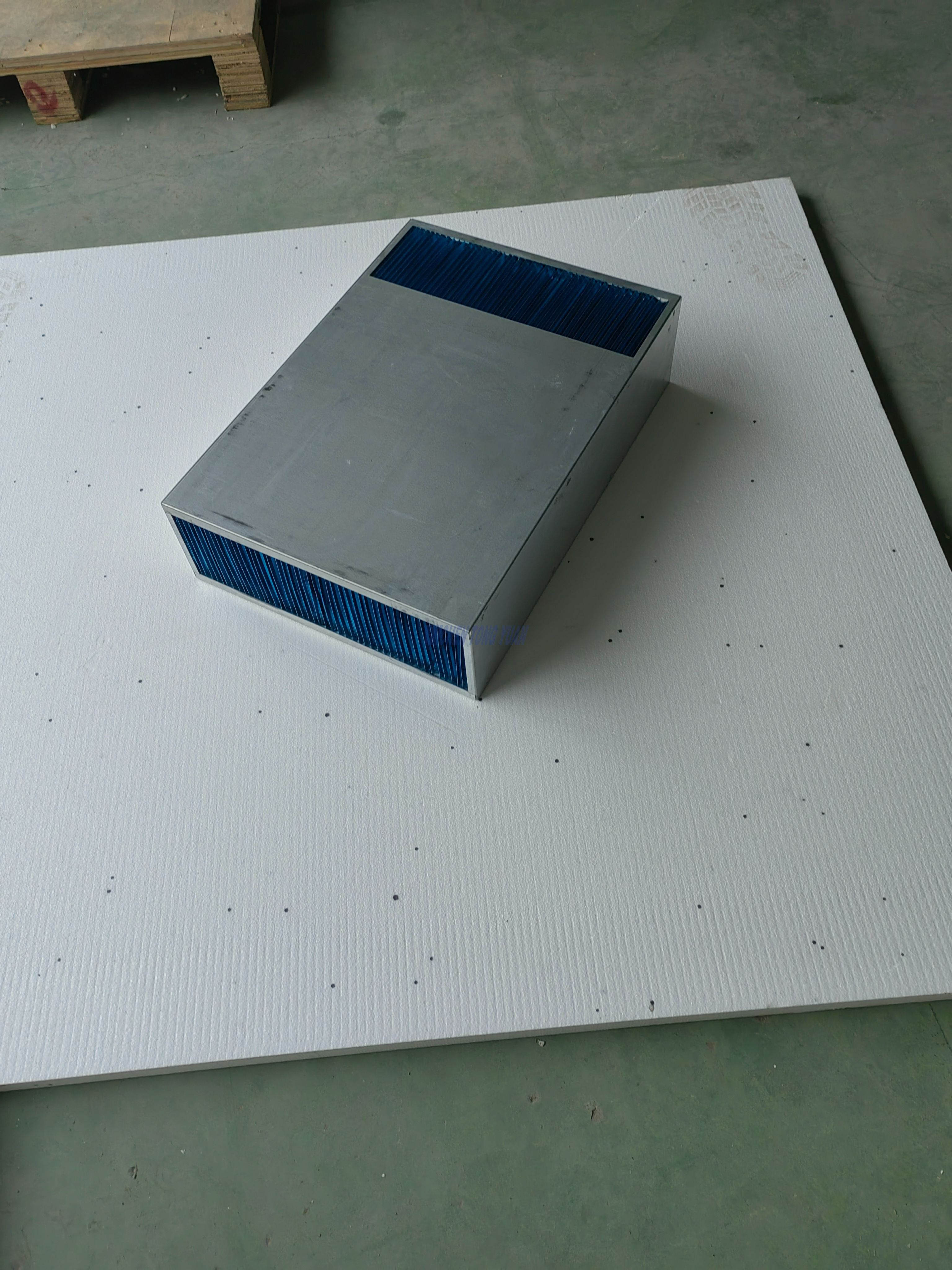
Optional size for the plate air to air heat exchanger core
| Model | Size A (mm) | size L mm | size B mm |
| CYCL90 | 90 | 200/250/300/350/400 | on-demand |
| CYCL95 | 95 | 250/300/350/400/450 | on-demand |
| CYCL140 | 140 | 300/400/450/500/550 | on-demand |
| CYCL180 | 180 | 350/400/450/500/550 | on-demand |
| CYCL190 | 190 | 400/450/500/550/600 | on-demand |
| CYCL225 | 225 | 500/550/600/650/700 | on-demand |
Characteristics of air to air plate heat exchanger
Enclosed air circuit cooling system design, which makes the inside air and outside air isolated and effectively avoids contamination from outside.
Avoid condensation due to excessively low temperatures.
Compact structure and convenient installation & maintenance.
It can be remote monitored.
Voltage range: AC220v, 50Hz/60Hz; AC110v, 60Hz; DC-48V.
The main components are international brands which greatly improves the reliability of the system.
Schematic Diagram of air to air plate heat exchanger
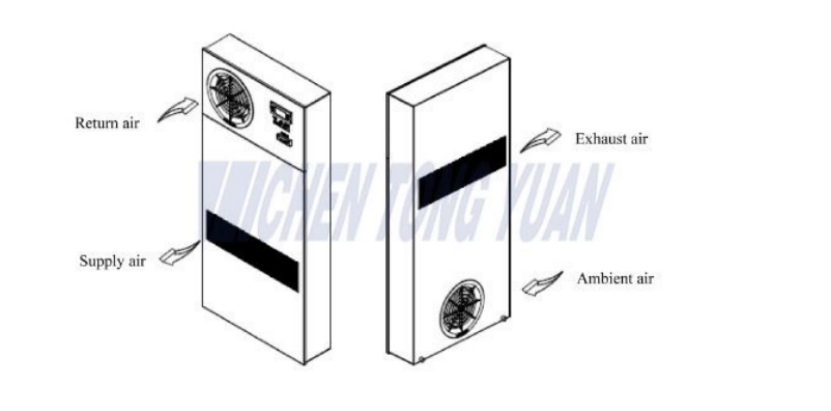
Type 2:Air-liquid-Air Heat Exchangers (Thermosyphon HEX)
Core Concept
A thermosyphon air-to-air heat exchanger is a type of passive heat exchanger that transfers heat between two separate air streams without using mechanical pumps or compressors. Instead, it relies on the natural circulation of a working fluid (usually a refrigerant or special liquid) inside sealed tubes to move heat from one side to the other.
Heat Exchange Core for air -liquid-air (Thermosyphon HEX)---Microchannel


Characteristices of Thermosyphon HEX
No moving parts → highly reliable and low maintenance.
Energy-efficient → doesn’t require external power for circulation (only fans to move air).
Air-to-air isolation → the two air streams remain physically separate, preventing contamination.
Works best when there is a temperature difference and the exchanger is installed vertically (to allow gravity return of the liquid).
Schematic Diagram of Thermosyphon HEX
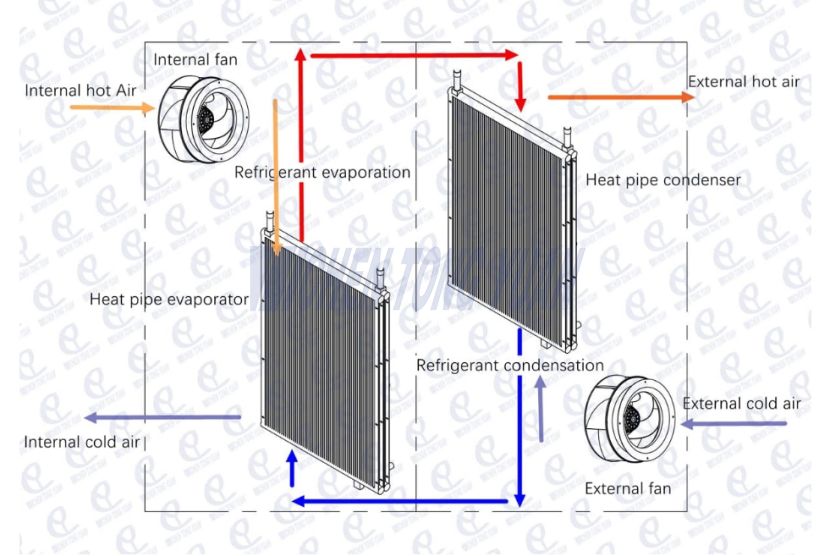
Both systems maintain a closed-loop cooling environment, meaning no outside air, dust, or humidity enters the cabinet
Communication Protocols for Cabinet air to air Heat Exchangers
Modern cabinet heat exchangers are not only about cooling performance; they also integrate smart monitoring and control systems. These systems allow operators to remotely manage temperature, alarms, and performance data. To achieve this, cabinet heat exchangers use different communication protocols.
 Standard Communication Protocol For DC Heat Exchanger V1.0.pdf
Standard Communication Protocol For DC Heat Exchanger V1.0.pdf
Cytech Cabinet heat exchangers typically support multiple communication protocols, including RS485/Modbus RTU, CAN Bus, Ethernet/Modbus TCP, SNMP, and Dry Contact. The choice depends on the application type, monitoring needs, and integration level with existing systems
Here are the most common types:
1. RS485 / Modbus RTU
Widely used in telecom and industrial applications.
Allows multiple devices to be connected in a network (multi-drop system).
Provides stable, long-distance communication.
2. CAN Bus (Controller Area Network)
Often used in automotive and industrial equipment.
Provides fast and reliable data exchange between devices.
Useful for real-time monitoring of cabinet cooling systems.
3. Ethernet / Modbus TCP
Supports IP-based communication over local networks or the internet.
Ideal for data centers, smart factories, and remote monitoring.
Integrates easily with SCADA systems and cloud platforms.
4. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
Common in telecom and IT cabinet environments.
Enables network managers to monitor equipment through existing IT systems.
Useful for alarm reporting and performance tracking.
5. Dry Contact / Relay Signals
A more basic communication method.
Provides alarm outputs (e.g., high temperature, fan failure) via simple electrical contacts.
Easy to integrate with existing control systems.
Why Do Cabinets Cooling Solutions Need Heat Exchangers?
Electrical enclosures protect sensitive equipment from external contaminants like dust, moisture, and dirt. However, they also trap the heat generated by the internal components. Without proper cooling, this heat builds up, causing:
Thermal stress on electronic components
Frequent breakdowns and downtime
Reduced equipment efficiency
Shortened lifespan of critical systems
Cabinet heat exchangers prevent these issues by maintaining a stable temperature inside the enclosure, ensuring optimal equipment performance.
Key Benefits of Cabinet Heat Exchangers
◆Energy Efficiency
Compared to air conditioners, cabinet heat exchangers consume significantly less energy. They use natural heat transfer methods, which makes them an eco-friendly and cost-effective cooling option.
◆Low Maintenance
Air to Air Heat exchangers have fewer moving parts and no need for refrigerants. This design reduces maintenance requirements and extends operational reliability.
◆Dust and Moisture Protection
The closed-loop system ensures that contaminants such as dust, dirt, and humidity cannot enter the cabinet. This makes them ideal for harsh and outdoor environments.
◆ Longer Equipment Life
By regulating temperature and eliminating overheating risks, heat exchangers help extend the service life of expensive electronic and electrical equipment.
◆Quiet Operation
Unlike air conditioning units, heat exchangers operate quietly, creating a safer and less disruptive working environment.
◆Cost Savings
Reduced energy consumption and lower maintenance costs result in long-term savings, making heat exchangers a smart investment.
Applications of Cabinetair to air Heat Exchangers
Cabinet heat exchangers are versatile and widely used across industries where equipment reliability is crucial. Common applications include:
Telecommunications: Ensuring stable temperatures for base stations, servers, and network equipment.
Energy & Power: Cooling energy storage cabinets, battery systems, transformers, and switchgear.
Industrial Automation: Protecting PLCs, drives, sensors, and other control systems from overheating.
Transportation: Providing reliable cooling for traffic control systems and railway electronics.
Renewable Energy: Supporting wind, solar, and hydroelectric equipment by keeping enclosures at safe operating temperatures.
Outdoor Installations: Suitable for harsh outdoor environments where dust, rain, and temperature extremes are present.
Data centers (energy-efficient air management).
HVAC systems (heat recovery ventilation, pre-cooling or pre-heating air).
Industrial enclosures (protecting machinery from overheating).
How to Choose the Right Cabinet Heat Exchanger
When selecting a cabinet heat exchanger, businesses should consider the following factors:
Cooling Capacity – Determine the amount of heat your equipment generates and choose a heat exchanger with adequate capacity.How to calculate cooling capacity ,please visit our other blogs for detailed instruction
Environment – Consider whether your installation is indoors or outdoors, and if it is exposed to dust, moisture, or temperature fluctuations.
Size of the Enclosure – Match the heat exchanger’s size and design to the dimensions of the cabinet.
Energy Efficiency – Look for models that reduce energy usage while providing effective thermal management.
Maintenance Needs– Choose solutions that minimize downtime and maintenance requirements.
Cabinet Heat Exchangers vs. Other Cooling Solutions
Businesses often compare cabinet heat exchangers with other cooling methods such as air conditioners or fan systems. Here’s how they differ:
Air conditioners consume more energy and require refrigerants, while heat exchangers are more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
◆Heat Exchangers vs. Fans:
Fans circulate air but allow dust, dirt, and moisture to enter the cabinet. Heat exchangers maintain a closed system, offering better protection.
Why Choose Cytech Cabinet Heat Exchanger for outdoor cabinet cooling?
Cytech cabinet heat exchangers are engineered for durability, efficiency, and adaptability. Here’s why customers choose Cytech:
◆High Reliability Materials
High-Quality Materials – Built with corrosion-resistant metals for long-term performance.
Galvanized steel ,Stainless Steel ,Aluminium for selection
Compliance with High temperature and humidity testing
High Temperature and Humidity Testing & Visual Inspection
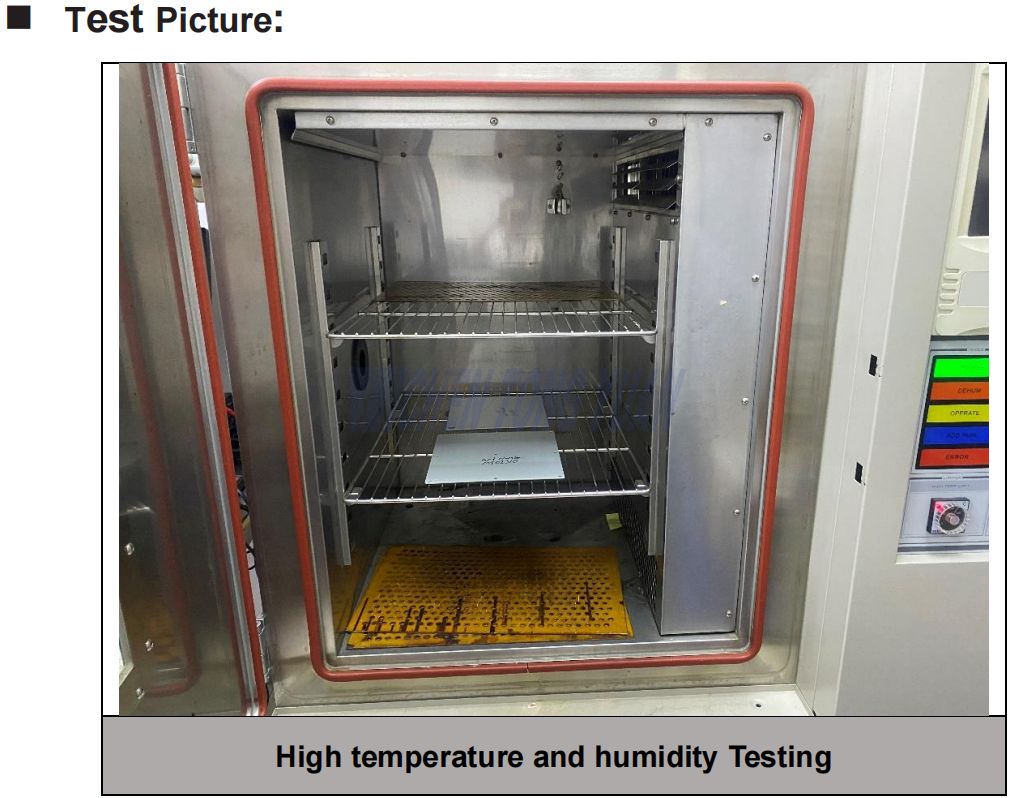


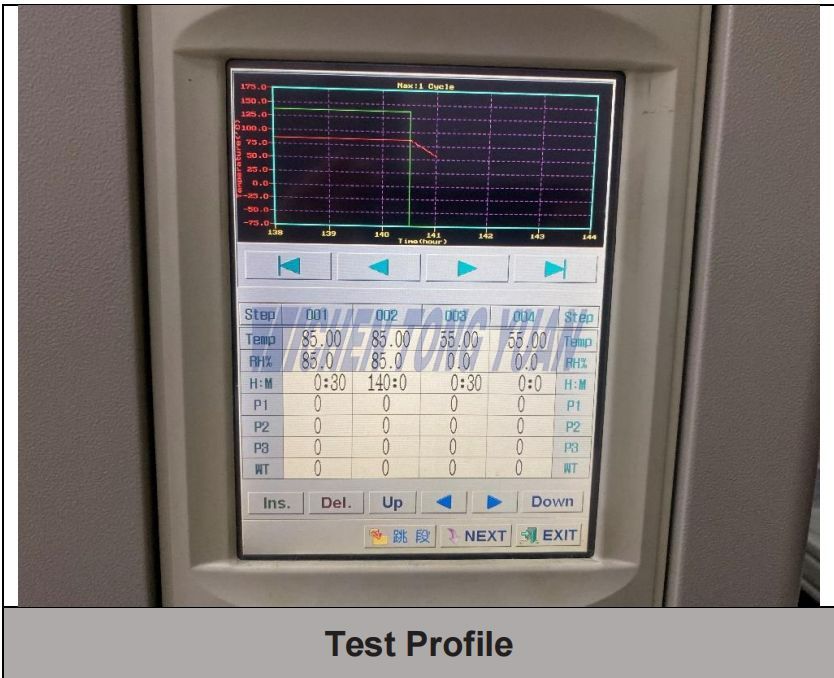
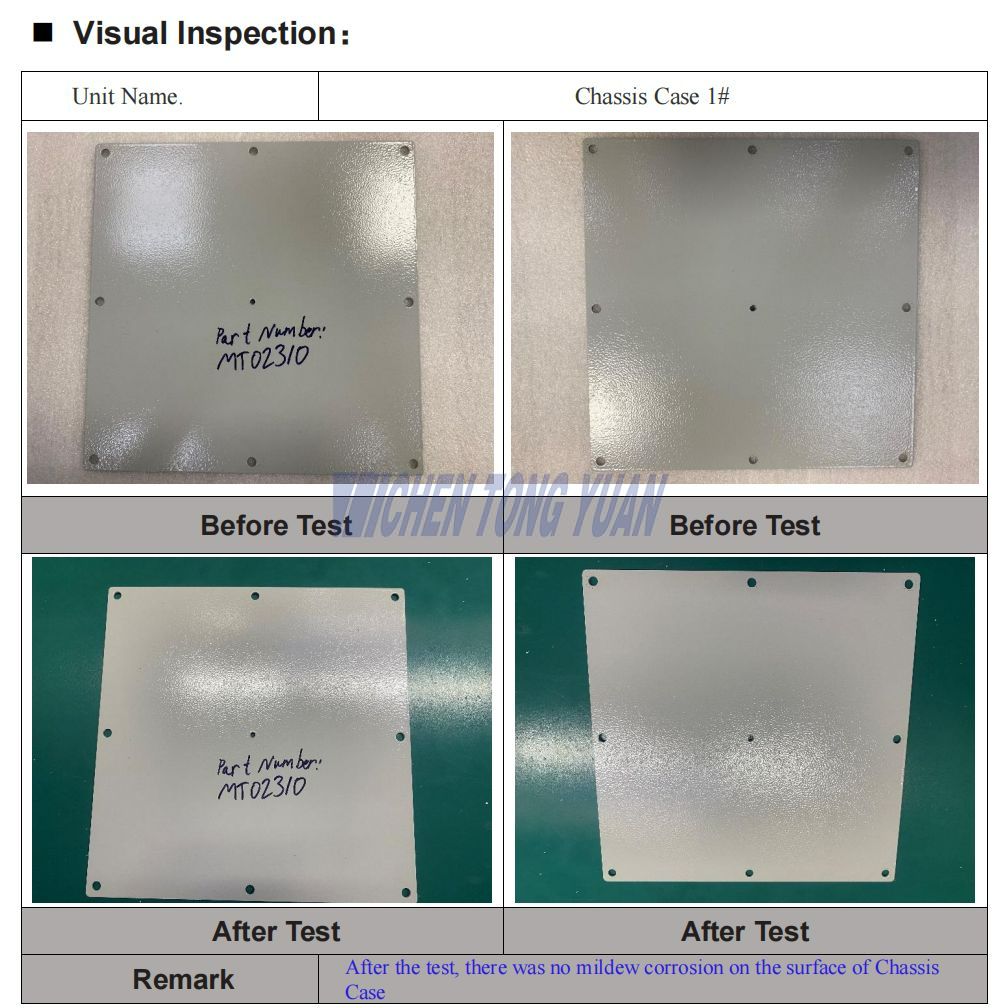
Testing Result : After the test ,there was no mildew corrosion on the surface.
Compliance with Salt Fog Testing &Visual Inspection
Salt Spray Tester

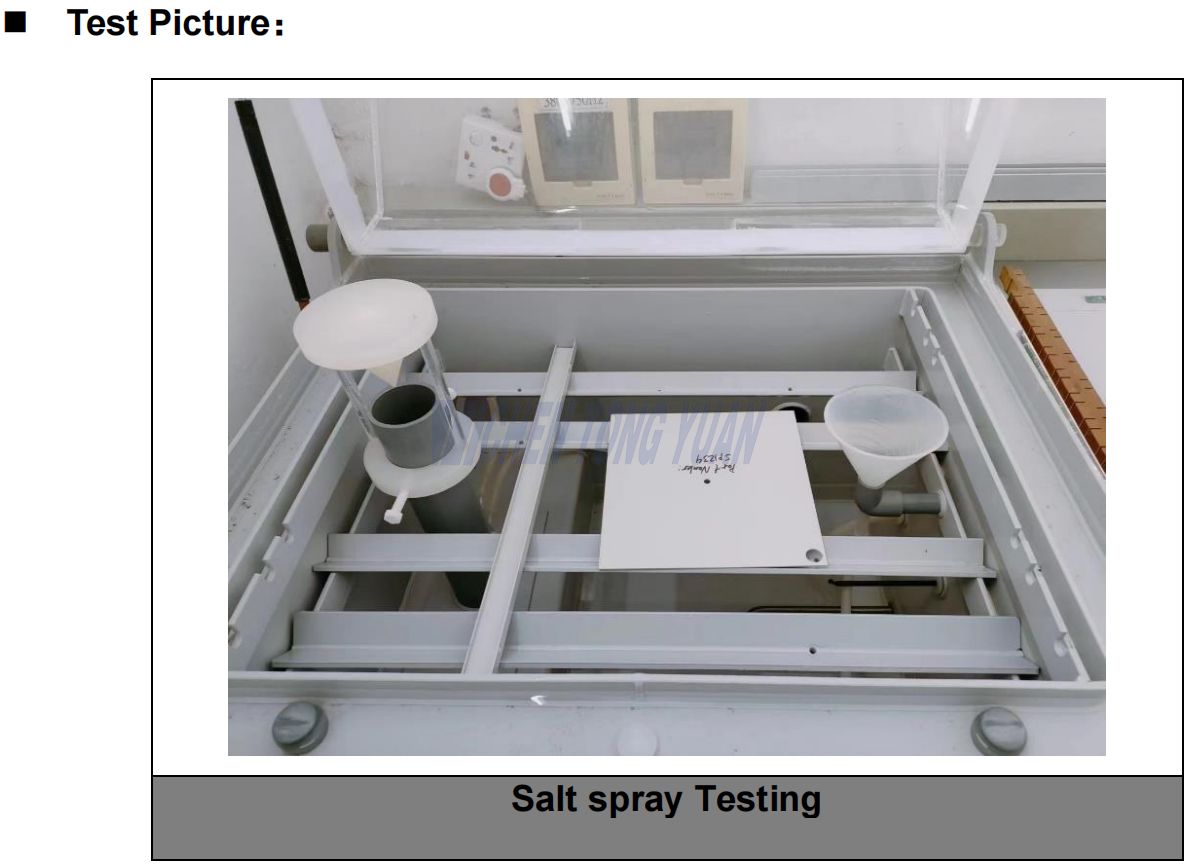

Testing Reslult :After the test, there was no mildew corrosion on the surface .
◆Customized Solutions
Custom Solutions – Tailored designs to meet specific customer needs.
Optional Fans -DC Backward Curved Centrifugal Fans
Optional heat exchanger Core --different size of Microchannel and HEX plates
Optional Models for Heat Exchanger |
Model | Heat Transfer
(W/K) | Rated Voltage
(V/ ph/ Hz) | Rated Power
(W) | Air Circuit
(m³/h) | HxWxD
(mm) | Weight
(Kgs) |
HEX-50 | 50/k | 220/1/50 | 120 | 400 | 750×411×118 | 20 |
HEX-60 | 60/k | 220/1/50 | 190 | 500 | 750×411×118 | 20 |
HEX-80 | 80/k | 220/1/50 | 260 | 800 | 1177×410×154 | 25 |
HEX-100 | 100/k | 220/1/50 | 260 | 900 | 1177×410×154 | 25 |
HEX-120 | 120/k | 220/1/50 | 330 | 1100 | 1237×410×154 | 28 |
HEX-150 | 150/k | 220/1/50 | 330 | 1300 | 1358×555×195 | 34 |
HEX-200 | 200/k | 220/1/50 | 360 | 2000 | 1520×600×198 | 38 |
Other cooling capacity cabinet heat exchanger |
◆International Standards
Compliance with International Standards – Ensures safety and performance in global markets.

◆Energy -Saving Technology
Energy-Saving Technology– Lower energy costs without compromising performance.
◆Customer Support
Reliable Customer Support – Dedicated service to assist with selection, installation, and maintenance.
Regular maintenance of a cabinet heat exchanger ensures stable cooling performance, protects sensitive equipment, and reduces operating costs. By following a simple cleaning and inspection routine, businesses can avoid unexpected downtime and extend the lifespan of both the heat exchanger and the valuable electronics inside.Here are some steps
How to Operate air to air Cabinet Heat Exchanger ?– Procedure & User Manual Guide
1. Pre-Operation Checks
Before switching on the heat exchanger, perform these checks:
Ensure the cabinet door is properly closed to maintain internal air circulation.
Confirm that the power supply matches the rated voltage and frequency of the unit.
Check that the air inlets and outlets are free from dust, obstructions, or blockages.
Verify that the communication interface (if applicable, e.g., Modbus, SNMP) is properly connected.
2. Start-Up Procedure
Power On: Switch on the main power supply.
Fan Activation: The internal and external fans will automatically start to circulate air.
Heat Transfer Begins: The thermosyphon or heat pipe cycle transfers heat from inside the cabinet to the outside air.
Control System Monitoring: If the model has a digital controller, the display will show cabinet temperature, alarms, and system status.
3. Normal Operation
During standard operation:
The heat exchanger runs continuously to maintain a stable cabinet temperature.
Temperature sensors monitor cabinet air and adjust fan speed if the model supports variable-speed fans.
Communication protocols (RS485/Modbus, SNMP, Ethernet) can be used for remote monitoring.
Some units provide alarm outputs (e.g., over-temperature, fan failure) via dry contact or relay.
4. Shut-Down Procedure
Switch off the main power supply when the cabinet is not in use.
Allow the fans to stop completely.
For maintenance, disconnect the power and follow safety precautions outlined in the user manual.
5. User Manual Availability
Cytech provide a user manual with every cabinet heat exchanger. A typical manual includes:
Product specifications (model, power rating, airflow, capacity).
Installation guide (mounting, electrical wiring, airflow direction).
Operation procedure (start-up, normal running, shut-down).
Safety precautions (electrical safety, handling instructions).
Maintenance instructions (filter cleaning, fan checks, inspection schedule).
Troubleshooting guide (alarm codes, error handling).
If you purchase a unit, always request the official user manual from the supplier or manufacturer for safe and correct operation.
Step-by-Step Maintenance Guide for Cabinet Heat Exchangers
1. Inspect the Unit Regularly
Check the heat exchanger every 1–3 months, depending on your environment.
Look for dust buildup, corrosion, or unusual noises.
2. Clean the Air Filters
Most cabinet heat exchangers come with protective air filters.
Remove and clean filters with compressed air or replace them if worn out.
A clean filter ensures proper airflow and reduces strain on the cooling system.
3. Clean the Heat Exchanger Surfaces
Dust and dirt often accumulate on the fins or coils.
Use a soft brush, vacuum, or compressed air to gently clean the surfaces.
Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage protective coatings.
4. Check for Airflow Blockages
5. Inspect Seals and Gaskets
6. Monitor Temperature Performance
Regularly monitor the cabinet's internal temperature.
If temperatures rise despite cleaning, the heat exchanger may need servicing or replacement.
7. Professional Servicing
Schedule professional maintenance once a year.
Technicians can perform deeper inspections, check for corrosion, and ensure efficiency.
Best Practices to Extend the Life of Your Cabinet Heat Exchanger
→Install the cabinet in a shaded or cool area to reduce external heat load.
→Use high-quality filters for better dust protection.
→Maintain proper grounding to avoid electrical damage.
→Keep a maintenance log for tracking service schedules.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the main purpose of a cabinet heat exchanger?
A: Its primary purpose is to remove heat from inside an electrical enclosure and keep equipment operating at safe temperatures.
Q2: How is a cabinet heat exchanger different from an air conditioner?
A: Unlike air conditioners, heat exchangers don’t use refrigerants and consume less energy, making them more eco-friendly and cost-effective.
Q3: Can cabinet heat exchangers be used outdoors?
A: Yes, many models are designed for outdoor use, providing protection against rain, dust, and extreme weather.
Q4: What industries benefit most from heat exchangers?
A: Telecommunications, energy storage, industrial automation, and renewable energy are some of the top industries that rely on them.
Q5: How often do heat exchangers need maintenance?
A: They require minimal maintenance, usually just periodic cleaning to ensure optimal performance.
Q6: Are cabinet heat exchangers energy efficient?
A: Yes, they are significantly more energy-efficient than air conditioners and fans, reducing operational costs.
Q7: Can I customize a cabinet heat exchanger for my application?
A: Absolutely. Cytech offers custom solutions to fit specific cooling needs and enclosure designs.
Q8: How often should I clean a cabinet heat exchanger?
A:Every 1–3 months, depending on the dust levels and environment.
Q9: Can I wash the heat exchanger with water?
A:It's best to avoid water. Use compressed air, a vacuum, or a soft brush.
Q10: What happens if I don't maintain the cabinet heat exchanger?
A:Dust buildup reduces cooling efficiency, increases energy use, and risks equipment overheating.
Q11: How do I know if my cabinet heat exchanger is failing?
A:Signs include higher cabinet temperatures, frequent equipment shutdowns, and unusual noise.
Q12: Do cabinet heat exchangers require professional servicing?
A:Yes, an annual professional check is recommended for long-term performance.
Conclusion
In industries where precision, efficiency, and reliability are essential, cabinet heat exchangers play a critical role in protecting equipment from heat damage. They are energy-efficient, low-maintenance, and designed to withstand harsh environments while extending the life of sensitive electronics. From telecommunications to renewable energy, these systems ensure that operations remain smooth, safe, and cost-effective.
By investing in the right cabinet heat exchanger, businesses not only protect their equipment but also achieve long-term savings and operational stability.






























